“What is Legionellosis?” and “How it is properly treated?” are the most common question asked by newly affected patients. Let us discuss about Legionellosis in detail.
What is Legionellosis?
Legionellosis is a medical condition ranging from mild febrile illness to severe conditions such as pneumonia. The extreme conditions are sometimes not curable. It is a bacterial infection caused by legionella species. The most common causative organism is legionella pneumophila.
Legionella species are present in water and potting mixes. Legionella pneumophila is mainly found in fresh aquatic bodies. As freshwater is primarily used for drinking and cleaning purposes, it is easily accessible to most individuals. This infection is caused by inhaling the aerosols formed from the water or soil infected with the bacteria. These aerosols or mist may be produced through air conditioning units, showers, or hot tubs. Legionnaires’ disease is not contagious, i.e., it does not spread from one person to another.
Legionellosis is a broad category of disease that includes three conditions: Legionnaires’ Disease, Pontiac fever, and Pittsburg pneumonia. As legionnaires’ disease is the most common among the others, legionellosis is frequently referred to as Legionnaires’ Disease.
Legionnaires’ Disease:
Legionnaires’ disease is a bacterial infection caused by the bacterium legionella. It is a severe infection of the lungs, also called pneumonia. This condition can be fatal.
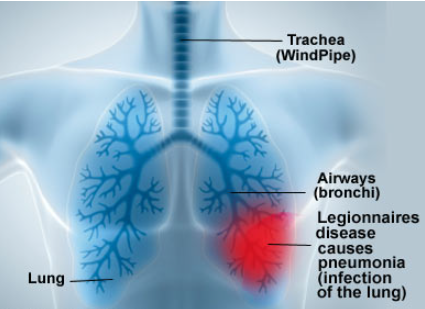
Pontiac fever:
Pontiac fever is a milder form of the disease. It is non-fatal and has no signs of pneumonia.
Pittsburg pneumonia:
This condition is similar to legionnaires’ disease but differs in its causative organism. The bacterium responsible for Pittsburg pneumonia is Legionella micdadei.
Signs and Symptoms:
The incubation period of legionnaires’ disease, on average, is around 2 to 10 days, but it can extend up to 20 days in rare cases. The incubation period is the length of time between exposure to the infective organism to the appearance of the early symptoms.
Initially, most people have these symptoms:
- High fever (104 F /40 C or higher)
- Headache
- Chills
- Myalgia – muscle aches
Other signs and symptoms that develop later, i.e., around the second or third day, are:
- Cough – dry or productive. A dry cough does not contain mucus, whereas a productive cough has mucus. Some patients also have blood in their sputum.
- Chest pain
- Dyspnea – shortness of breath
- Malaise – restlessness
- Lethargy – tiredness
Different body systems are affected as a result of this disease. The systems involved and the symptoms related to them are as follows:
Gastrointestinal system:
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite – reduced desire to eat
Neurological system:
- Confusion
- Ataxia – Loss of coordination
- Cognitive impairment – inability to concentrate or learn new things.
Cardiovascular system:
Relative bradycardia – lower heart rate than average despite the presence of fever.
Already existing wounds in the body also get infected when someone suffers from legionnaires’ disease.
Pontiac fever has milder symptoms as compared to legionnaires’ disease. They usually last around 2 to 5 days. The patient experiences fever, headaches, restlessness, and muscle aches, but it does not cause pneumonia. It usually recovers without any treatment.
If a person presents with the symptoms persistent with legionnaires’ disease, they are evaluated further by some laboratory tests. Lab results show some signs to confirm the diagnosis and estimate the extent of the disease.
SIgns in Laboratory tests:
Lab tests that can be performed and their results to confirm the diagnosis of legionnaires’ disease are as follows:
- Urinary antigen test (UAT) – detects legionella bacteria in the urine.
- Sputum culture – the presence of legionella species in sputum
- Electrolyte levels – it will show low sodium levels in the body.
- Liver function test – elevated liver enzymes.
- Kidney function test – elevation of nitrogenous products in the body, excretion of blood and proteins in urine
- Complete blood count – elevated lymphocytes, i.e., white blood cells, presence of antigens against legionella.
- Chest X-ray – pneumonia with consolidation at the bottom of both lungs, i.e., a portion of lungs filled with liquid instead of air.
Complications of Legionnaires’ Disease:
Legionnaires’ disease is a life-threatening condition. If left untreated, it can lead to severe and debilitating health conditions that may lead to death. It has the following effects on the body:
- Severe pneumonia – causes the person to have difficulty breathing despite the normal oxygen levels in the environment.
- Septic shock – blood supply to essential organs is compromised due to sudden drop in blood pressure. The heart tries to compensate by increasing its activity, but the additional workload gradually weakens the heart and lowers blood flow even more.
- Respiratory failure – This happens when the lungs are unable to supply required oxygen to the body or remove waste carbon dioxide from the blood.
- Acute kidney failure – occurs when your kidneys lose their function. They are unable to filter waste from the blood. Kidney failure causes the body to accumulate toxic levels of fluid and waste.
- Multi-organ failure – causes severe pain and failure of two of the essential organs of the body, i.e., kidneys, lungs, and liver.
Legionnaires’ disease has mortality, i.e., a death rate of 10% in healthy individuals and 25% in immunocompromised individuals. However, it can be as high as 40-80% in immunocompromised individuals who do not get treated for the infection. With proper care and treatment, the mortality rate is dropped to 5-30%.
Who is susceptible to Legionnaires’ disease:
Healthy individuals are less likely to get ill from legionella infection as their body’s defense mechanisms are strong enough to fight against diseases. Individuals are more likely to get sick if they have:
- Advanced age, i.e., 50 years or older.
- Chronic lung infection – emphysema, COPD
- Smokers – are susceptible to all kinds of lung infections.
- Immunocompromised individuals – with a weak immune system that may be due to some medical condition or some therapy or medications
- Other medical conditions – include diabetes, kidney disease, and cancer.
Prevention and Treatment:
There is no vaccine available against legionnaires’ disease. Prevention can be done by reducing the growth of legionella species. It can be achieved by good maintenance of the water systems.
A bacterial infection is treated using antibiotics and other medications to relieve symptoms. The most effective antibiotics for treating legionnaires’ Disease are Levofloxacin, Azithromycin, and Doxycycline.
Tell us in the comments, how you like our article “What is Legionellosis?”
For similar posts like this, click here.
For the source file, click here.
You may also like
Scoliosis Disorder
In this article, we will discuss all about “Scoliosis Disorder”. So, let’s dig deep to find all about the different causes, signs, and treatment of this ailment. Scoliosis is a disorder in which the spine curves to the side abnormally. Several distinct variations of scoliosis can affect children and young adults. Idiopathic cancer is the… Continue reading Scoliosis Disorder
Various Treatment Options for Osteoporosis
In this article, we will discuss all the “Various Treatment Options for Osteoporosis”. So, let’s dig deep to find all about the different signs and symptoms of this ailment. Osteoporosis causes bones to become weak and brittle, rendering them vulnerable to fractures from even slight forces such as coughing or leaning over. Osteoporosis-related fractures most… Continue reading Various Treatment Options for Osteoporosis
Various Symptoms of Osteoporosis
In this article, we will discuss all the “Various Symptoms of Osteoporosis”. So, let’s dig deep to find all about the different signs and symptoms of this ailment. The disease known as osteoporosis causes the bones to gradually lose their dense texture, strength, and resilience as one gets older. According to information provided by the… Continue reading Various Symptoms of Osteoporosis
Birth Defects from Smoking
In this article, we will discuss all the “Birth Defects from Smoking”. So, let’s dig deep to find all about the effects of smoking on a newborn children. The majority of individuals are aware that smoking can lead to cancer and other serious health problems. Additionally, smoking during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk… Continue reading Birth Defects from Smoking
